Using MS Cleaner
To run the program go to Start / All Programs / MS Cleaner, and click on the MS Cleaner icon.
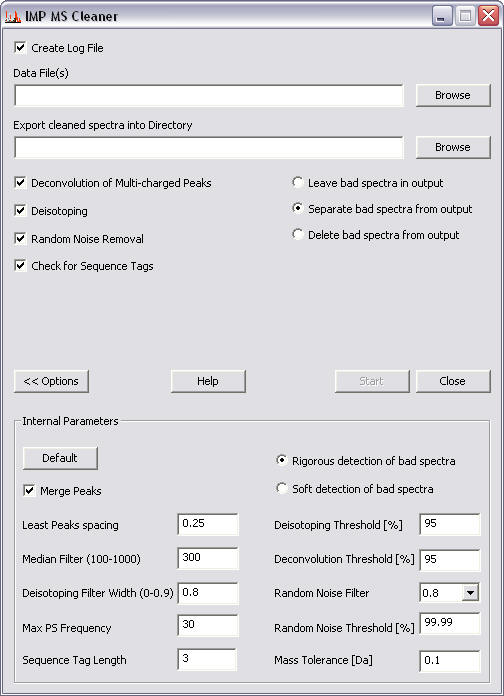
When the program is run, the user interface dialog box appears. This enables the user to chose the parameters for the MS cleaning procedure.
To explore the user interface, click on a feature of interest in the figure below.

| User interface control elements | Description |
|
|
Selecting this check box will result in generation of log file, which for each spectrum records the results of the cleaning procedure.
This file is saved in the ..\cleaned\ directory.
|
|
|
This edit box displays the input data files to be cleaned. Either type in the path name of a single file, or click the browse button to select file(s) from an open file dialog box.
Supported data formats are: - Sequest files (*.dta), single spectra - Mascot generic files (*.mgf), multiple spectra
|
|
|
This edit box displays the directory into which the cleaned spectra will be saved. By default, the program creates a ..\cleaned\ directory within the directory chosen for the input data files.
Alternatively type in the path name of the directory or click the browse button to select a directory from an open directory dialog box.
The program creates cleaned files in the same format (*.dta or *.mgf) as the input data file.
The name of the cleaned file is the same as the input data file, with an additional "_c".
|
|
|
If selected, the program detects multi-charged isotope peak clusters according to the chosen Deconvolution threshold. These are then transformed into a single monoisotopic peak. All other signals from the cluster are deleted.
|
|
|
If selected, the program detects singly-charged isotope peak clusters according to the chosen Deisotoping threshold. These are then transformed into a single monoisotopic peak. All other signals from the cluster are deleted.
|
|
|
If selected, the program removes random noise from the spectrum according to the Random noise threshold.
|
|
|
When this option is selected, the program inspects each MS2 spectrum for a series of peak spacing with m/z values corresponding to amino acids mass (with certain mass tolerance) - known as a sequence tag. The user can define the length of the sequence tag in the accompanying-box (values in the range 2 to 5 are recommended). The presence of a sequence tag indicates that the spectrum is likely of protein origin. Spectra without a sequence tag (likely derived from non-protein polymer contaminants) are classified as 'bad'.
|
|
|
Determines bad spectra handling.
Selecting the first option will leave spectra designated as "bad" in the "cleaned" output file. Using this option doesn't separate bad spectra from remaining files.
Selecting the second option creates two sets of output file(s): cleaned files (minus the bad spectra), and bad spectra files, which are saved in a new directory ..\badspectra\, within the ..\cleaned\ directory. The name of the bad spectra file is the same as the input data file, with an additional "_bad_c".
Selecting the third option deletes the bad spectra from the output files.
|
|
|
Clicking this button opens and closes a form allowing user to change the internal parameters.
|
|
|
Clicking this button invokes this document.
|
|
|
Resets the internal parameters to their default values.
|
|
|
If selected, the program merges together peaks that are closer than the Least Peaks Spacing value.
|
|
|
Specifies the least allowed spacing between peaks for the Merge peaks algorithm of the program.
|
|
|
Specifies how many signals are taken for median filtering of the power spectrum.
|
|
|
Specifies the deisotoping filter width.
|
|
|
Specifies the maximum allowed frequency of the power spectrum.
|
|
|
Starts the cleaning procedure.
|
|
|
Closes the dialog box and quits the program.
|
|
|
This mode is used to find the highest possible number of bad spectra and reduce the amount of data as much as possible. Although some spectra are bad, they can still be interpreted by a database search program. With this option, removal of bad spectra can lead to a lower sequence coverage, but a higher confidence in the interpretation.
|
|
|
Using this option, fewer bad spectra will be identified. This mode is used if a high sequence coverage is more important than data reduction.
|
|
|
The deisotoping procedure reduces the intensity of the potential isotope peaks. If the decrease in intensity is greater than this threshold value, the intensity of the peak will be set to zero.
|
|
|
The deconvolution procedure detects multi-charged peaks if the correlation coefficient is higher than this value.
|
|
|
This is the stop frequency for the low pass filter used for random noise removal.
|
|
|
This filter reduces the intensity of random noise peaks. If the decrease in intensity is greater than this value, the intensity is set to zero.
|
|
|
Specifies the length of the sequence tag.
|
|
|
Mass tolerance taken into account during the sequence tag determination.
|
After the cleaning procedure has been completed, the following message box appears:
Clicking on OK removes this box and returns the focus to the main program window, allowing further cleaning operations to be performed.